| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
The first thing we want to know is how the tree did in general:
...
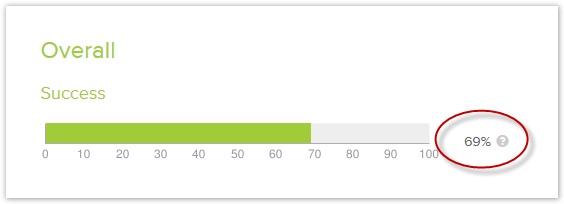
Not surprisingly, the most important thing to look at is success rate – how many participants chose the correct answer, across all tasks?
Most tools will give you us this as a rating out of 10 or 100. For example, a score of 69 means that 69% of the time, participants chose a correct answer:
Once you we see a tree’s overall success rate, the natural question is “Well, is that good, bad, or just average?”
As If you have a previous tree test to compare with, the answer is easy–at least if the trees and tasks cover the same functionality. (No fair comparing between tests with different tasks or different content.) The score is "good" if it's better than the last time you tested. This is one of the advantages of a tree test; it's relatively easy to benchmark your current structure against alternatives, and to iterate quickly. So if you hadn't planned on setting a baseline, maybe reconsider; it's much easier to make a case for change if you can show improvement.
If you don't have a previous test to compare against, you're back to wondering if it's good, bad, or average. And as any consultant will tell you, the answer is: it depends. Mainly, it depends on two things:
...
- 0-50 – The tree needs to be completely rethought or discarded.
Trying to tweak it will only bring it up to “mediocre”. - 50-65 – The tree needs substantial revisions.
If your our analysis reveals specific problems (and it should), and you we think you we can fix them, you we should be able to revise this tree to perform well. - 65+-80 - The tree is effective, but may need minor revisions.
Your Our participants are finding the correct answer at least two-thirds of the time, so the tree is doing its job well, and only needs tweaking.
- 80+ - Either the tree is very good, or the tasks are too easy.
We don't see many well-constructed tree tests with scores over 80. It does happen, but we really should review our tasks to make sure they're not too easy, and that we're not giving away answers by word matching.
| Warning |
|---|
| A high score doesn’t mean “no revisions needed”. We’ve never run a tree test where everything worked so well that we couldn’t improve it a bit more. There are always a few lower-scoring tasks that suggest further improvements. |
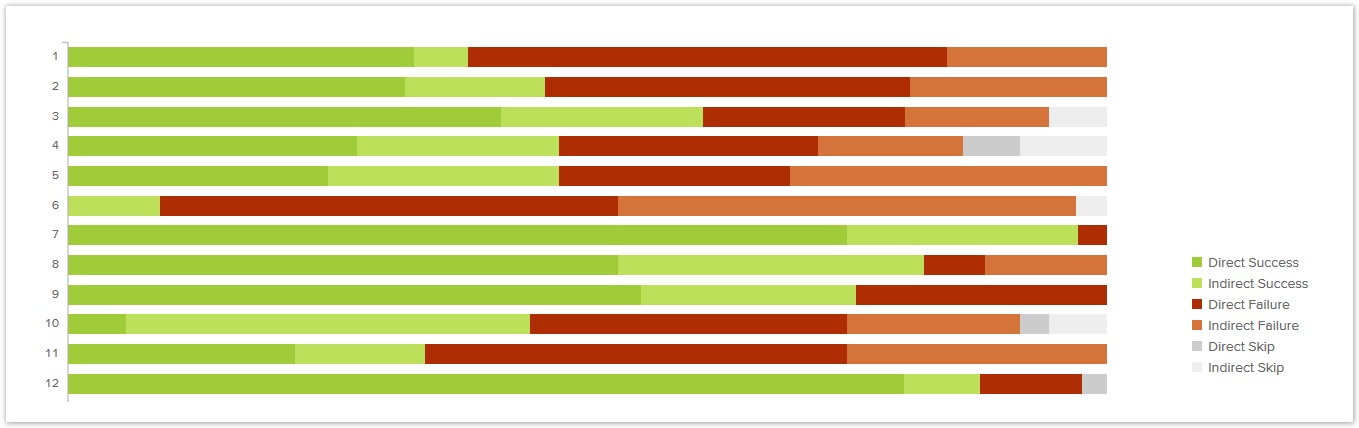
What the overall success rate doesn't tell you us is how much the success rate of the individual tasks varied. For example, a 60% overall score may mean that all tasks hovered around 60%, or that half your our tasks were 90% and half were 30%. To find out, you , we need a breakdown by task, which some tools summarize in a graph like this:
In this example, we can see that a few tasks had very low success rates, and two were very high. To find out more, we need to drill down to the task level - see Task success rate later in this chapter.
Comparing tree-test scores to usability-test scores
People are often surprised that we consider 65+ to be a "good" score. Shouldn't we set the bar be set at 80 or 90?
Effective trees don't usually score higher than 80 because we're testing a top-down text-only tree with no other aids. Our participants are making choices without the benefit of:
- other navigation aids such as see-also links, featured links, and multi-level browsing (e.g. mega menus)
- visual design - chunking of links/content, and emphasis on more important links/content
- content that explains headings using decoration text, hover text, etc.
Once we refine our text tree to be effective (i.e. perform well in tree testing), we should then be able to add these other design elements to further improve the findability of items in our website.
| Tipinfo |
|---|
| In our experience, success rates from the final website tend to be 20-30% ~20% higher than the scores we see in tree testing. |
Lisa Fast at Neo Insight has written an ~interesting blog post an interesting article comparing tree-test scores to usability-test scores. HereHere's a graph showing what she found:
the graph of how they related in her study:
Lisa found that not only were the two scores correlated, the usability-test scores were 29% higher (on average) than the tree-test scores.
Finally, we should warn that adding other aids is no guarantee of improvement. A poor visual design, clumsy navigation, or sub-par content can actually make a website perform worse in usability testing than it did in tree testing. A single method can only go so far. ![]()
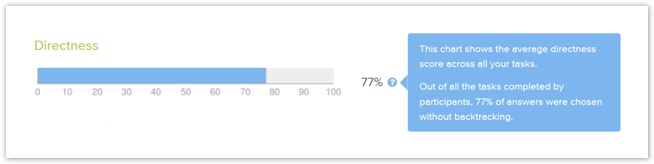
Overall directness (backtracking)
To get a general idea of the effectiveness of your our tree, it also helps to look at how directly your our participants found the right answer. Did they go straight there, or did they have to try a few different paths first?
How this is scored depends on the tool you’re we’re using:
- Some tools treat directness as a simple yes/no measure – did the participant backtrack at all during a task? This method doesn’t care if they backtracked 1 time or 5 times during the task – it’s either yes or no.
In our experience, 70% is an average score for this method. Less than that indicates that users are having trouble finding the right path. - Some tools try to quantify how much wandering a participant did. A single back step lowers their score a bit, but repeated meanderings through the tree lowers it much more.
~guidelines for scores using this method?
While the overall directness score gives you us a rough idea of how clear and distinguishable your our headings are, you’ll we’ll need to drill down to specific tasks to determine where the most backtracking happens. For more on this, see Directness – where they backtracked later in this chapter.
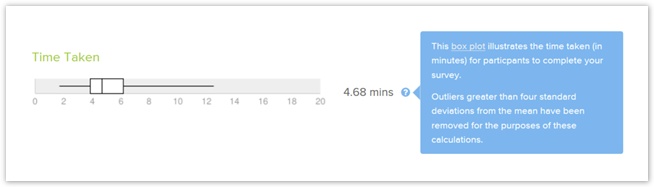
Overall speed (time taken)
Most tree-testing tools show you us the average (or median) time taken by your our participants to complete the tree test.
Comparing times between trees
If you’re we’re testing several trees against each other, and the trees are approximately the same size (in breadth and depth), you we can compare these overall times to see if some trees are “slower” than others. This suggests that participants either had to:
...
This is a very rough measure, however, and to make sense of it, you’ll we’ll need to drill down to see which tasks (or specific areas of the tree) are slowing down your our participants. For more on this, see Task speed - where they slowed down later in this chapter.
Keeping
yourthe study brief
A more practical use for the average time taken is making sure that your our tree test is not taking too much of your the participants’ time.
In general, we recommend an overall duration of 5 minutes for a tree test. This is typically how long it takes the average participant to do 8-10 tasks (our recommended amount) for a medium-size tree (200-500 items).
If you we have a larger tree, your our test time may exceed this, but we still recommend that you keep keeping it under 10 minutes to avoid participant fatigue and boredom.
If your the average duration is longer than this because you we are asking each participant to do a lot of tasks (say, 12 or more), you we are likewise inviting participant fatigue and boredom. More importantly, your our results may be skewed by the “learning effect” – see How many tasks? in Chapter 7.
A “total” score
Some tools present a single overall score, combining several measures: success rate; directness; speed; and so on. This overall score typically uses some kind of weighting, with success rate usually being the biggest factor.
...
- Treejack calculates its overall score as a weighted average of success rate and directness (at a 3:1 ratio), but does not include speed in its calculations. ~no longer provides a total score?
- UserZoomother tools?
...
Next: Analyzing by task